Live, build and renovate in a healthier way
Disclaimer: This article has ben written WITHOUT the use of AI by a living being, based on choosing peer-reviewed research and other source material. Still, errors can happen (in any way less than by the use of AI). Be critical, read through the further literature linked down below, and feel free to provide input in the commentary section. Good reading!
This is a long article that can be used as a reference work. IT IS STRUCTURED IN FIVE PARTS: 1. Introduction with an overview of environmental hazards 2. General guidelines in building biology 3. Hazardous substances and sources with examples, their recommended maximum values in building biology for sleeping areas as well as state limits and countermeasures. 4. Practical examples with pictures showing building biology implementation and solving challenges. 5. Sources, resources and further information. |
1. INTRODUCTION AND OVERVIEW

This is a water tank from the first century after Christ, year 79 (AD) from the Roman Villa Arianna in Pompeii. The era and the villa bear the mark of enormous wealth, art and technological progress. The tank itself was part of a bathing complex, you can see stopcocks to control the water supply and it is said to have been partially installed visibly, with ornamentation on it. Simply an interaction of practical utility and elegance. There is only one flaw with this one: It is made of pure lead. A heavy metal that we know today is both carcinogenic and dangerous to both humans and the environment.
You may (not) be surprised when I point out that this is still a problem in today's building methods, something I will come back to. Our society can be compared in many ways to the Roman Empire at this time: At the height of wealth, unparalleled abundance, technical sophistication so advanced that you don't even know what to use it for, art that is so abstract that only a few understand it, domination of other societies with high-level warfare. Unknown health challenges that we can't find the source of despite a "top" health system. Since I am am writing about practical and technical solutions so that YOU can live healthier, I shall refrain from politicizing any further about how such wealth and ignorance could lead to the collapse of a society within a few generations.
Back to lead. Not only lead is a challenge today, but a sea of other environmental toxins in houses and house installations:
- Plastics that release disease-causing chemicals such as Bisphenol A (BPA), Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), artificial hormones (Estrogen – especially in plastics marked “BPA-free”) and currently about 40,000 other substances that are largely unknown. Microplastics that are released from plastic parts in the house and that accumulate in the body.
- Electromagnetic fields and radiation exposure from non-ionizing radiation (electrical wires, WLAN, routers and access points, IOT – internet of things, smarthome solutions, smart meters) that damage cell nuclei and cell division (reproduction), create problems in signal transmission in the brain and peripheral nervous system and weaken the immune system.
- Heavy metals and neurotoxins such as lead, arsenic and nickel from the house’s water installation. In other words, heavy metals and neurotoxins that are both carcinogenic and lead to general signs of illness and a weakened immune system.
- Chemicals (VOC) from adhesives in construction (chipboard, visible surfaces, cabinets and kitchens), oils and varnishes (surface treatment, paint), materials (vinyl flooring).
- Mold spores that are introduced through airtight construction methods that trap moisture, especially when renovating older buildings incorrectly.
- Dry air from balanced ventilation that attacks mucous membranes and makes the body more susceptible to bacterial and viral infections.
- Artificial light from LED bulbs that, through their "chopped" on-off lighting and their unnatural color spectrum that only "seems" to illuminate like natural light, save electricity but disrupt our visual system and affect the nervous system as well as other biological processes in the body.
Behind all of the above-mentioned problem areas stand peer-reviewed research showing a connection towards serious health conditions such as allergies, hormonal disorders, developmental damage in children and adolescents, cancer, late-life damage in old age such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, undiagnosed conditions such as headaches, migraines, fatigue, exhaustion, and increased susceptibility to other diseases.
For many of the above-mentioned environmental toxins, there are no real minimum requirements in today's building regulations (e.g. Norwegian TEK17), or they are so broad that they have no practical significance in reducing dangers.
Fortunately, there are foreign, building biology recommendations for sleeping areas. An example is the German Institute for Building Biology and Sustainability (IBN).
2. GENERAL GUIDELINES IN BUILDING BIOLOGY
Here is an excerpt from their 25 guidelines in building biology:
Indoor climate
- Reduce pollutants and ensure sufficient fresh air
- Avoid harmful mold and yeast, bacteria, dust and allergens
- Use neutral and pleasant-smelling materials
- Reduce electromagnetic fields and radio waves
- Prefer radiant heat as a heat source.
Building materials and interior design
- Use natural materials free of environmental pollutants and with the lowest possible radioactivity
- Ensure a balanced ratio between thermal insulation, heat storage, surface and room temperature
- Use materials that balance moisture
- Ensure low humidity in new construction
- Optimize room acoustics and sound insulation, including infrasound (sound below 20 Hz).
Room design and architecture
- Ensure harmonious proportions and shapes
- Promote sensory impressions such as sight, hearing, smell and touch.
- Focus on natural lighting conditions and color, do not use flickering light sources
- Take into account physiological and ergonomic findings
- Promote regional building styles and craftsmanship
Environment, energy and water
- Reduce energy consumption and use renewable energy sources
- Avoid negative impacts on nature during construction and renovation
- Conserve natural resources, protect plants and wildlife
- Ensure the best possible drinking water quality
Ecosocial living space
- Ensure good use of infrastructure: Short distances to workplaces, public transport, schools, shops, etc.
- Design living spaces that are humane and environmentally friendly
- Plan sufficient green space both in the city and in the countryside
- Strengthen self-sufficiency and short distances, include suppliers and service networks
- Choose construction sites that are preferably not burdened with noise, pollutants and radiation sources.
Implementing these recommendations is possible without violating technical requirements and without having to break the bank, provided that the measures have been planned before renovation or construction. Some measures can still be implemented relatively inexpensively afterwards. Being able to actually measure values and see results and put them in context helps many people understand the importance.
3. HAZARDOUS SUBSTANCES, SOURCES, EXAMPLES, LIMIT VALUES AND MEASURES
In the following section I provide an excerpt from both SBM-2024 (standard for building biological measurement technology) guidelines from IBN (German Institute for Building Biology and Sustainability) and (Norwegian) interest organizations that apply the precautionary principle (e.g. FELO = Association for the electrically sensitive) as well as state limit values (e.g. DSA = Directorate for Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety; as well as Labour Inspectorate) and some reference values from nature and research. Rather than let industry decide (which conducts research with the premise that the products are harmless, which can be "proven" based on research methods and measurement setups and implement this via lobbying), we take nature as a starting point and are critical, until the opposite is proven.
The presented recommendations apply to sleeping areas. The limit values should also be taken into account for other areas where you spend a lot of time during the day, such as living rooms, home offices, workplaces, kindergartens and classrooms in schools and universities.
Fields, waves and radiation
Electrical alternating fields
These are fields including the power grid, power cables in the house, extension cords, cables for lamps, dirty current from chargers and other electronics.
|
Measures:
- Get a detector for "LF" radiation such as Gigahertz Solutions ME 3830B or HF/LF Cornet. The Cornet is recommended for most people. It could also be rented from interest organizations such as FELO or EMF Consult AS in Norway.
- Do not use unshielded extension powercords at the head of the bed or sitting/office areas.
- Use shielded cords for lamps at the bedside and office area.
- For new installations or renovations, use shielded industrial cables in the installation (e.g. Lapp Ölflex).
- Choose switches with a two-pole break (both conductors in the cable break in the "0" / off state).
- Install a mains disconnect in the fuse box to make parts of the house voltage-free when there are no consumers in operation.
- Use a mains filter where dirty current (electric car charger) is a problem.
Magnetic alternating fields
Is a by-product of the power grid (see above), but especially also transformers, motors, pumps, heat pumps, compressors (refrigerators), etc. which should not be in the immediate vicinity of the bed and sleeping area anyways.
|
Measures:
- Same recommendation regarding the detector device as above.
- Largely the same as for electric alternating fields.
- With distance, the exposure decreases quickly, so make sure to take physical distance, e.g. by repositioning the bed or head end.
- Avoid exposing yourself to magnetic fields such as using an electric car if you are particularly susceptible.
Electromagnetic waves, high frequency
WLAN / WiFi, mobile networks, mobile Internet, LTE, 4G, 5G, IoT (Internet of things – washing machines and refrigerators that are app-controlled), TETRA (emergency communication), AMS meters (which in Norway use a continuously active mesh network instead of transmitting once a day via the power grid), bluetooth, DECT, radio, TV, radar.
The problem with the measurement unit used here is that it is based on heating of tissue over short time intervals (not long-term effects!). It is an outdated measurement method that is not particularly relevant anymore: The danger comes from biological effects, DNA changes and the formation of free radicals (highly reactive molecules that lead to oxidation and degradation of cell membranes, proteins and genetic material = enormous potential for damage in the body). The European Council and a number of other organizations and research groups are calling for a change in the current limit values due to alarming findings.
In addition, a measurement method is used that only shows average load (over time), but not maximum load that pulses (PEAK). The latter has major consequences on activation at the cellular level, which cannot be measured with average values.
|
Measures:
- Get a detector type "Cornet", a simple "all in one indicator", or "Safe and Sound Pro 2" for HF. For mm-waves (above 20GHz) you would need a "Safe and Sound Pro mmWave Meter". You can also borrow such devices.
- Physical distance to radiation sources such as mobile towers and other radiation sources.
- If this is not possible because moving is not an option, apartments and especially bedrooms can be shielded with shielding paint (expensive). This job must be done correctly so as not to increase the radiation load due to, among other things, reflection.
- Shielding baldachin (made of conductive material) over the bed / office space.
- Require disconnection of the transmitting module in the AMS meter. FELO can provide guidance here.
- Install a wired network in the house with a router that does not transmit wirelessly.
- Wire PC/computer and mobile phone and tablet (USB to Ethernet adapter).
- Refrain from using all devices that use WLAN, Bluetooth, Smart solutions and Internet of Things (IOT). Possibly rebuild or modify these if you have the knowledge, which will lead to loss of warranty.
Radioactivity
In contrast to the low-energy, electromagnetic radiation mentioned above (so-called non-ionizing radiation), radioactivity is high-energy, ionizing radiation. It lies on the other side of the light spectrum. Radioactivity has a completely different effect on the body and cells, and requires different measuring equipment. We will not go into detail here, in Norway the main challenge is the isotope Radon from rocks that can come through the floor in basements and rooms.
The aim is to have a below 50% impulse or dose rate increase, which depends on the gamma radiation in your environment. In Norway, it is approximately 100 nSv/h (Nanosievert per hour = dose equivalent), "background radiation". |
If you use a Geiger counter that measures in R (Roentgen), this corresponds to 11.5 μR/h (Microroentgen per hour). I am fully aware that the conversion of these units is not scientifically correct (a bit like "apples and pears"), but it holds up for our purposes.
|
Measures:
- For emergency preparedness purposes, a good quality Geiger counter is a sensible investment. Being able to measure radon exposure requires though knowledge and special equipment. It is not worthwhile for most people. You can order test kits online or rent equipment to take radon measurements.
- Good mapping during construction with an effective radon barrier, possibly a well and control measurements.
- For other radioactivity, physical distance or shielding are the only effective measures. Unless you live in a very exposed area, where moving is the best solution, sheltering will be most relevant in crisis situations. However, this falls under crisis preparedness and the use of shelters or basements. Further information here.
Sound waves / noise
The overall goal is that no disturbing sounds or vibrations should be present. These can come from traffic, loud music, industrial noise, train and air traffic, but also in the house from e.g. heat pumps, circulation pumps and fans. These can create resonance that propagates through the building. Remember that the unit of measurement is logarithmic, i.e. an increase of 3 dB corresponds to a doubling of noise. Similarly, a reduction of 3 dB means a halving of sounds.
|
For mobile phones, there are several free APPs that measure sound levels and can provide average values. These are not calibrated and do not measure infrasound. There are also often several decibel deviations between the measurements. Here, a so-called (expensive) "class 1 meter" is needed.
Infrasound can also be picked up and analyzed by smartphone with the App "RedVox".
For technical installations, the noise requirements that existed when they were installed apply. In the current regulations, there are 4 classes (A-D), where there is only a requirement for sound class C in new homes. Class A is the strictest.
Possible measures:
- Choose a heat pump that meets the building regulations' noise requirements. Possibly create a screen.
- Set up a noise fence between you and your neighbor's outdoor heat pump.
- Ensure that circulation pumps, fans, refrigerators or freezers and other vibrating motors are mounted so that they do not transmit vibrations to the supporting substructure.
- Soundproof noise sources in the house/apartment with healthy solutions, not foam boards made of recycled plastic (see below regarding VOCs, solvents). For example, Hunton wood fiber insulation has very good soundproofing properties.
Light / artificial lighting
| The sleeping area should be as dark as possible, ideally 0 lux. 2-3 hours before sleep, the light sources should be adjusted to natural light in the evening twilight. The light should correspond to the natural light spectrum, without an excessive blue light proportion, but with a high infrared proportion. Flicker should be as low as possible and it should not produce electric or magnetic fields. |
In practice, this means halogen or old incandescent bulbs which, in contrast to modern LED lighting, produce a lot of heat (IR proportion) and a natural color spectrum similar to sunlight.
Today's requirements for reduced electricity consumption lead to the widespread use of LEDs and in the EU/EEA even a ban on the import and production of halogen bulbs. Modern lighting with a high blue light content inhibits melatonin production needed for sleep, increases the number of free radicals that accelerate disease development and inhibits the formation of ATP (energy production in the body) that uses infrared light. Flicker is also a major problem for people with epilepsy.
There are several LED products (warm white, Philips Ultra Definition, red light bulbs) on the market that are not supposed to have a blue light content, flicker, etc. At the time of writing, I haven't found enough evidence-based studies to support such technology. It is quite possible that these light sources may be a suitable alternative!
Measures:
- Living rooms and offices / work spaces should be designed so that they let in as much daylight as possible.
- Where this is not possible, rooms should only have as much artificial light as is necessary to carry out tasks.
- During the day, one should expose oneself to natural daylight as often as possible.
- Only use incandescent bulbs / UV protected halogen bulbs at desks, bedside lamps or other places where you spend a lot of time.
- Ensure good light insulation in bedrooms, especially children's rooms. This means the room should be dark at night, do not have lights on.
- There are measurement results on YouTube in tests of several types of "multispectrum LED bulbs" and the necessary measuring equipment that connects to data via USB can be purchased relatively cheap. However, it would be for those who are particularly interested people.
Solvents and other volatile environmental pollutants
So-called VOCs (volatile organic compounds) are found in almost all types of sprays, chemicals, construction foam, XPS and polystyrene boards, paint products and surface treatments, cleaning agents, furniture, building materials made of plastic. They are also found in perfumes, mold (!) and "new car smell" is a classic example of VOC emissions.
|
Be particularly critical of strong-smelling, allergenic, irritating and carcinogenic substances in the air such as Benzene, Naphthalene, Styrene, Phenol, Dichloroethane.
Measures:
- Actively search for products that have low VOC, be critical of all unnatural substances. Do not settle for explanations from retailers or for products that "have low VOC", "approved by the EU" or similar.
- Swan-labeled products tend to have lower VOC concentrations.
- Especially for paint, there are good alternatives if you choose, e.g. lime paint.
Be critical of "cheap" or "modern" solutions such as ready-made chipboard, polystyrene as insulation material, or other materials that require covering / sealing after installation.
Sprays and other semi-volatile contaminants
Both pesticides such as Permethrin, DDT, pesticides, flame retardants, plasticizers such as Phthalate and PCB are found on dust particles, in the air or on materials that have skin contact. They are therefore expressed in concentrations of milligrams per kilogram.
| The recommendations (SMB) for these vary by type of substance and are at concentrations of 0.5 mg/kg and above. |
Measures:
- Since it is difficult to measure these substances for the average person, the recommendation here is to not use of these substances.
- With regard to combating pests such as ants, wasps or mosquitoes, find good solutions in terms of construction technology or ensure sufficient ventilation when using them.
- Flame retardants in furniture and curtains should be avoided by choosing products that are clearly labeled.
- Completely refrain from using pesticides (Round Up). Instead, choose planting or design that suppresses weeds or removes them physically, e.g. by burning (propane gas burner).
Heavy metals
These are metals with a certain density (over 5 g/cm³). The most well-known heavy metals are: lead, cadmium, chromium, iron, gold, copper, manganese, nickel, mercury, silver, zinc, tin, tungsten.
Some heavy metals are very toxic, even in small concentrations.
|
Here we return to history in the introduction about the water supply made of lead from Roman times. We know that heavy metals cause reproductive damage, cancer, allergies and sensitization, but for now we only have common values as references values. Apply the precautionary principle and limit these substances as best as possible.
This is particularly relevant in the water supply. The house installation for drinking water is today mainly made of plastic (plastic pipes which themselves are questionable with regard to PVC, BPA, microplastics and artificial hormones that plastic secretes) as well as brass connections, fittings i.e. fixtures / taps, valves and couplings. These parts release a surprisingly large proportion of metals into the water, even though they constitute a relatively small proportion of the installation.
The most common material in Norway is dezincification resistant brass (DZR brass). It consists of 62% copper, 36% zinc, 2% lead and 0.1% arsenic (a nerve poison!). Lead is added to improve the machining process during the production of the parts. Lead is then released into the drinking water for usually 2-3 months and then decreases, but corrosion can lead to a sharp increase again later. The corrosion can be caused by local water conditions or errors in the installation.
A regulation is being worked on with a upper limit value for lead content in brass of 0.3% by 2030.
Nickel is also released into drinking water, as most taps and visible fittings and parts are surface-treated with chrome (nickel underneath, and also on water-bearing surfaces on the inside due to production processes). Measurements show emissions into the water for 1-2 years, but nickel is measurable even after many years.
Measures:
- Let the water run for 2-3 seconds from the tap, especially if the water has been standing still, e.g. overnight.
- Carry out regular water sampling that you send to a lab for assessment of the pollution on drinking water.
There are test strips for heavy metals that are similar in design to pH tests or urine sticks. However, these test strips are not very accurate. Measuring devices are expensive and rarely necessary for an assessment in private homes. - When installing new / replacing, choose installation material made of gunmetal (red brass), stainless steel or lead-free brass instead of dezincification resistant (DZR) brass.
- Prefer stainless steel taps and fittings instead of chrome-plated ones.
- Filter systems, either gravity-based or RO filter systems (reverse osmosis), filter heavy metals, chemicals and wires as well as microplastics. These are available as stand-alone filters or for installation under the sink or as part of the water installation in the technical room.
- Water distiller also removes heavy metals but are often more expensive to purchase and use (electricity costs).
Particles and fibers
| Particle, fiber and fine dust concentration in the room should be at the same level or below the corresponding outdoor level. Asbestos and mineral fibers should not be present in dust at all. |
Measures:
- Vacuum cleaner with HEPA filter, or central vacuum cleaner. Robot vacuum cleaners are currently equipped with HEPA filters but the machine itself should not use WLAN, Bluetooth or radar technology (see fields, waves and radiation further up).
- When renovating or installing new insulation, avoid using mineral wool (such as glass wool or rock wool, which irritate the respiratory tract and emit dangerous gases such as formaldehyde in the event of a fire) but instead choose healthy natural products such as wood fiber insulation (e.g. Hunton wood fiber insulation), which can be processed without protective clothing and inhaled without the risk of lung damage.
Room climate / indoor climate
| Relative humidity should be between 40 and 60%. |
This can be a challenge, especially in newer buildings with balanced ventilation that prevents natural regulation. But also massive wooden structures (log houses / log houses), especially in combination with a wood stove in operation in winter (where it is dry outside) can lead to low humidity.
| Smell: There should be no individually annoying smells present. |
Measures:
- Get a simple hygrometer, either digital or analog and set it up centrally in the house / apartment.
- Humidifier. There are many different types that vary in quality and differ in terms of capacity, covered area and the way water is atomized, which in turn can introduce bacteria and algae into the room air.
- Ventilation systems are a requirement in modern buildings. These can be avoided by a traditional construction method that ensures natural ventilation.
Fungi, bacteria, allergens
Mold, yeast
| There must be no fungi present indoors, either visibly or using a microscope. |
Deviations and suspicions can be detected through color changes of surfaces, stains, typical smell, moisture damage, poor hygienic conditions, illness of residents.
Measures:
- Aggressive total sanitation if found. The most effective measure is the physical removal of the nutrient medium instead of trying to combat fungi with chemicals.
- Avoid prolonged increased material and air humidity, too cool surfaces and critical cold bridges.
Bacteria
| Bacteria should also be absent, or lower than the corresponding bacterial load outdoors. |
Suspicions can be detected in the same way as with mold. It is particularly important to protect critical areas such as drinking water, hygiene, bathroom and kitchen areas.
Measures:
- Bacteriological examination of the drinking water. Water test sent to the lab.
- Use of water filters that filter bacteria and viruses out of drinking water. There are a number of different filter types depending on needs and preferences: UV light, freestanding filters with ceramic elements that work using gravity without electricity, RO filter systems (reverse osmosis) that filter most harmful substances and have a long lifespan, distillation devices (evaporate water and capture the water vapor).
Dust mites and other allergens
| There are currently no building biology guidelines. |
Lab values and allergy experts can be consulted if suspected and needed.
4. PRACTICAL EXAMPLES
In the following we will look several ways of implementing building biology recommendations and improving living conditions.
Renovation of a city apartment with high EMF exposure from mobile phone masts in the immediate vicinity.
The owner complained about migraine-like symptoms with headaches when she was siting on the sofa in the living room. Physical effects could be easily reproduced and measurements showed 886 μW/m² at head height on the sofa (recommended building biology limit value 1-10μW/m², depending on source). Note that the measuring device is of an older type and did NOT pick up 5 GHz and above, this was before the rollout of the 5G network, so actual measured values are even higher.
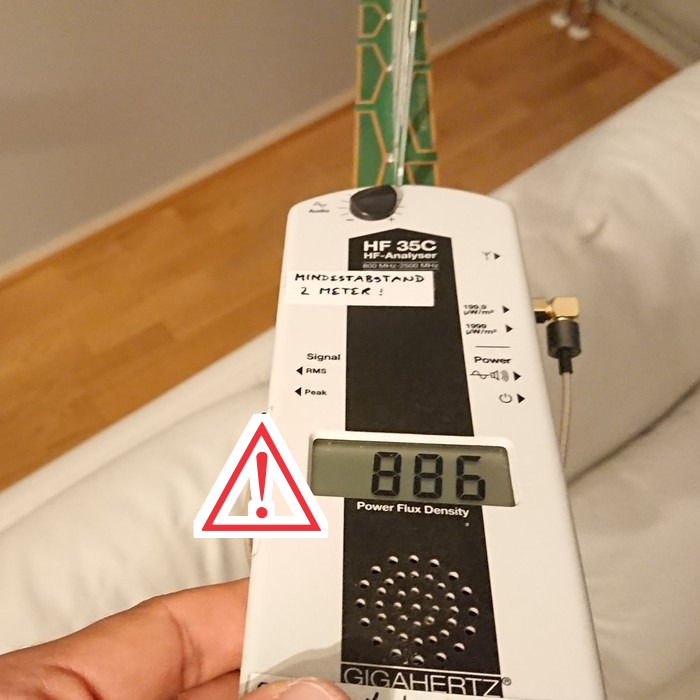

The mobile transmitter installation is well integrated (read camouflaged), installed on a parking garage just 60m away from the apartment. In the upper right corner you can see office spaces that are located around 15m from the transmitter in an exclusive location. The radiation values here are somewhat lower than through the wall as the window has a built-in metal film against solar heating. However, a lot of radiation leaks through the window frame and the wall.
The Sonos speaker on the window bench is unplugged and therefore does not radiate during the measurements. Later, the wireless module from it was removed.
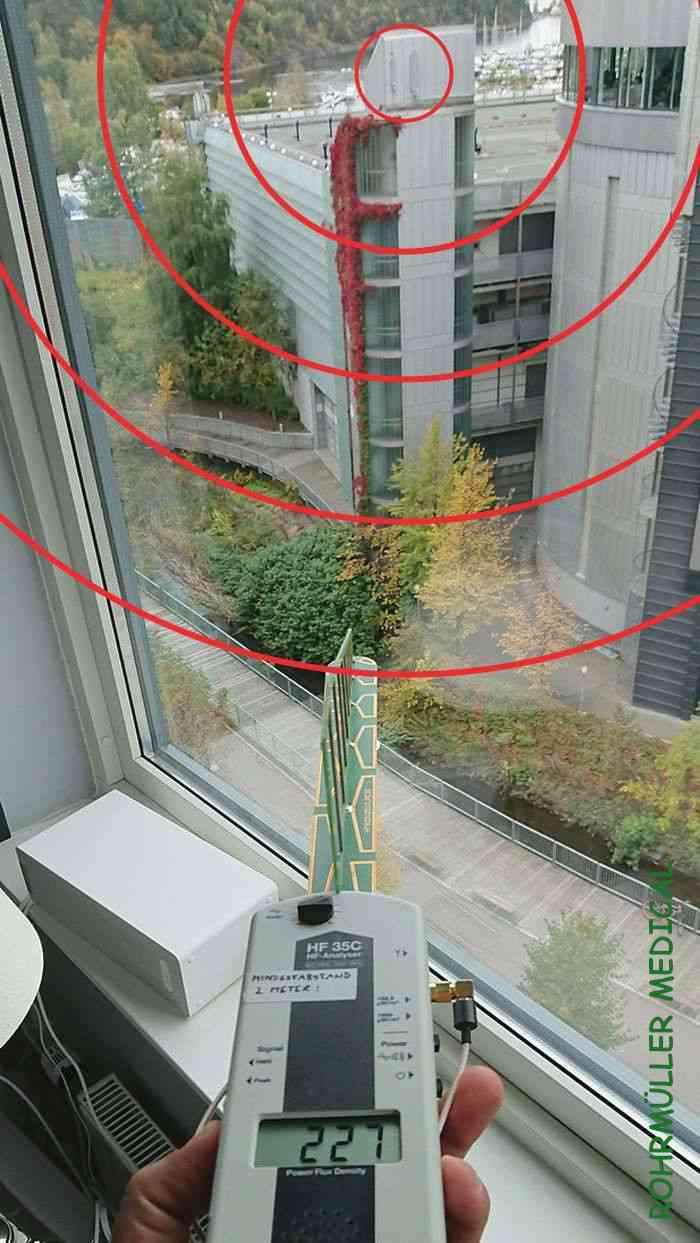

Here you can see the radiation level directly under the same window showing the effect of the metal film in the window. A 4-fold increase compared to the window and a similarly high value as on the sofa:

Solution: The main wall was painted with a coat of graphite paint (type "Yshield" supplied by EMF Consult AS) and grounded in accordance with regulations. Graphite is a highly conductive material and shields well against high-frequency radiation. It is easy to apply, can be painted over and is harmless from a chemical assessment (VOC).

The effect was immediate and interesting: The radiation values almost doubled! This is a good example of why control measurements are important and why it is necessary to choose the right remediation measures.
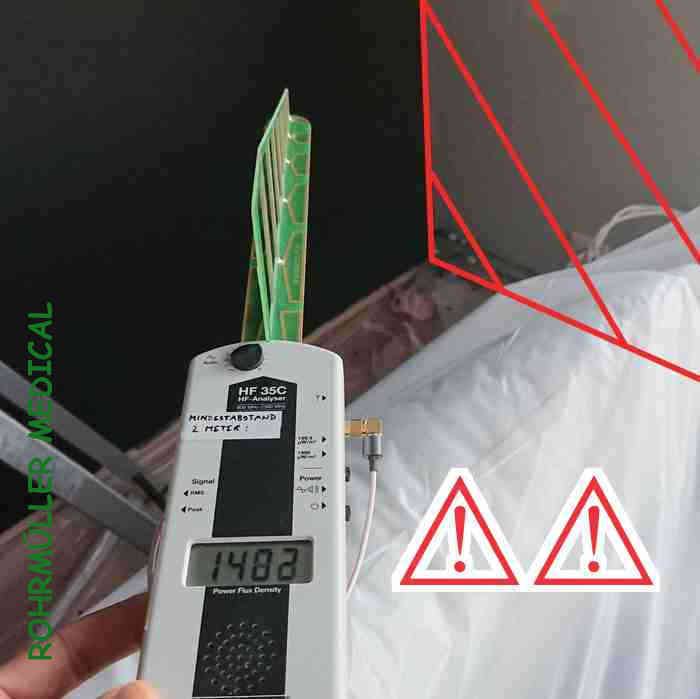

But why? - The reason is twofold: The wall on the right side had not been shielded, so the radiation was still leaking in. In addition, radiation from a transmission tower on the opposite side of the shielded wall was now reflected back into the room.
The solution was to shield the room on all sides. The result was significantly better. Going from 886 μW/m² to 46 μW/m² (19 times lower!) is a real attenuation and the result was noticeable. Although the value is still well above the recommended 10 μW/m², it shows that it is possible to reduce high-frequency radiation even in such extreme environments. If one had also shielded the ceiling and floor (neighbor's WIFI), one could have achieved good levels. Since graphite paint was relatively expensive and the apartment had already been renovated, one chose to live with these values.
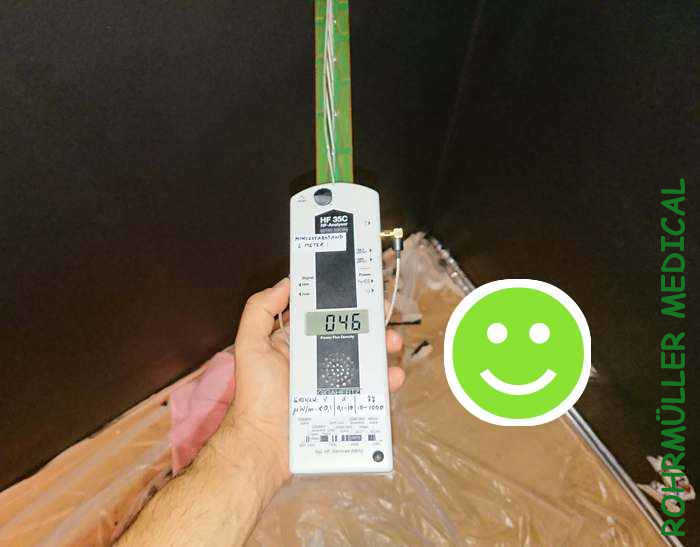

The walls were then over painted in the desired color.
Fortunately, the bedroom was not affected by this HF pollution. However, one should consider whether one wants to expose oneself to such radiation levels over time.
Wired network / Internet
To get internet access, one does not have to live with a WIFI router. One can easily plug a network cable into the router and use a wired network. NOTE! The router does not turn off the WLAN (WIFI) function just because you are using a cable.
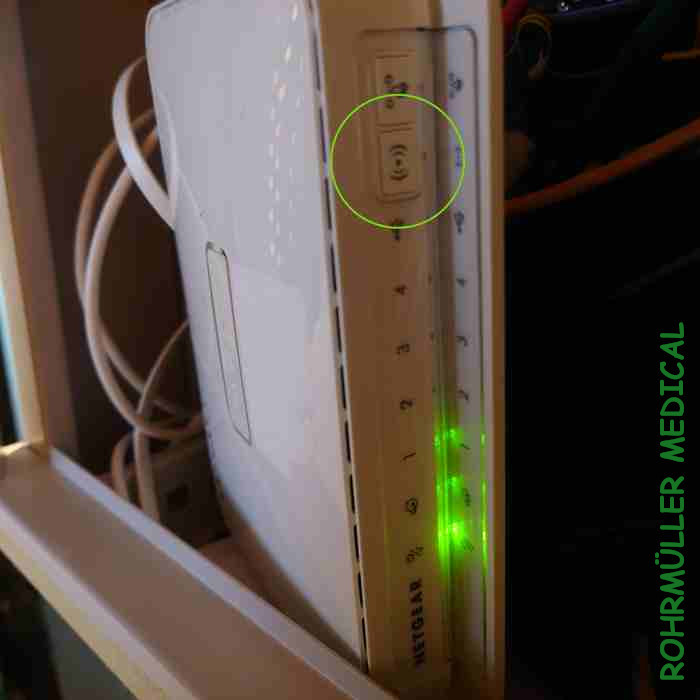
Modern routers also transmit on several frequencies / bands at the same time (commonly both 2.5 and 5 GHz). Some routers have a button that physically turns off the WIFI like this one, or you have to change its settings. Double check with a measuring device that the transmitter is really turned off. This also applies to printers and other devices that have an "on/off switch" for the transmitter.
You can also reasonably get a MUCH BETTER router by installing a Linux-based operating system on a cheap router. It will then have all the functions that are otherwise only reserved for expensive routers. The router loses its warranty, which is not a problem when it is bought cheaply on the second-hand market for a couple of 100 Norwegians crowns.
Some relevant functions you get are: Permanently turn off WIFI, change the transmission strength (dB) and connection interval (beacon) if you want WIFI in selected rooms / for guests without irradiating the entire apartment / house.

You also don't need to have network cables hanging throughout the house. There are thin but shielded (important) network cables that are easy to install in transparent cable channels so that the visual impression is not spoiled.

Smart phones / mobile phones can be connected to the network using a USB to Ethernet adapter. These are available for both Android and iPhone based phones. Adapters are available with USB-C, Lightning, Micro-USB plug on one end and Ethernet (RJ45) on the other end, often in combination with USB for parallel charging. They are inexpensive and can be purchased online or at Finn.no
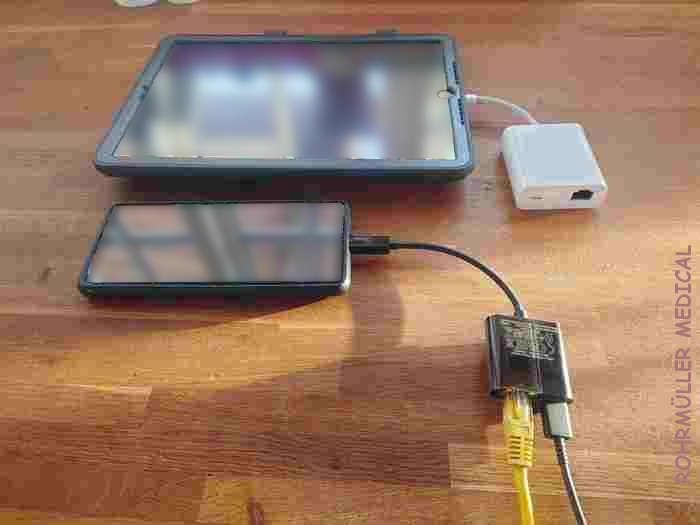

If you are planning the design of the house's technical installations, renovating an older building or building a new one, it is recommended to install a minimum of 2 network cables for every room. Alternatively, you can install empty pipes to run these later. This way you have enough leeway to adapt to future use, whether it is for your children, a home office or repurposing rooms.

Insulation and post-insulation of buildings
Without a doubt one of the best methods to save energy and your wallet in the long term.
When renovating a log cabin, I was looking for alternatives to felt strips. These are made of plastic, and apart from questionable health properties, I was looking for a design that fits the traditional construction method. Hemp could have been an alternative.
I would like to present here a much better solution as an insulation material that has been used for hundreds of years: Moss from the forest, more specifically glittering woodmoss or stair step moss (Hylocomium splendens). It is distinguished by having good insulating properties, does not retain moisture, is antibacterial and diffusion-open. It is also easy to handle and costs nothing if you have access to a forest / permission from the landowner. This type of moss grows in "stair steps" per year, often over stones, hence the name. It is important to choose the right type of moss to get this effect.
During the rehabilitation of the building, we found this type of moss that was over 100 years old, in as good condition as new, both in terms of texture, color and smell.
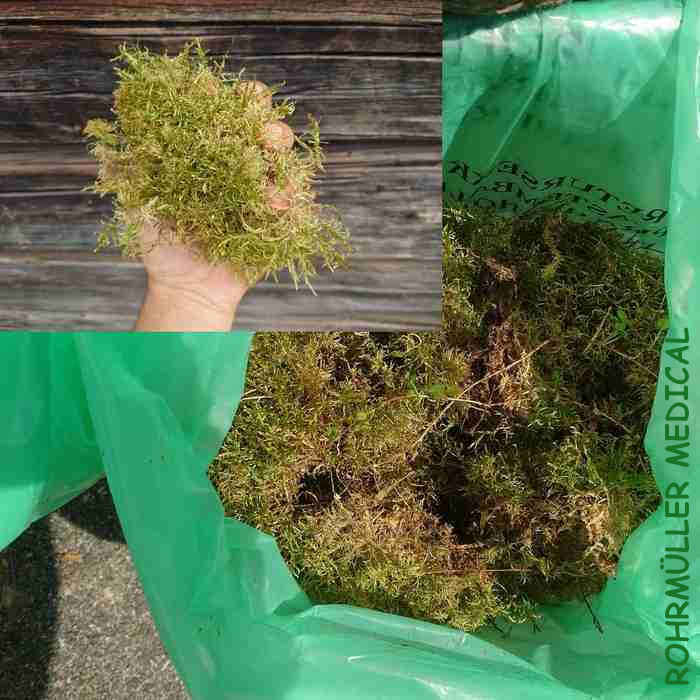
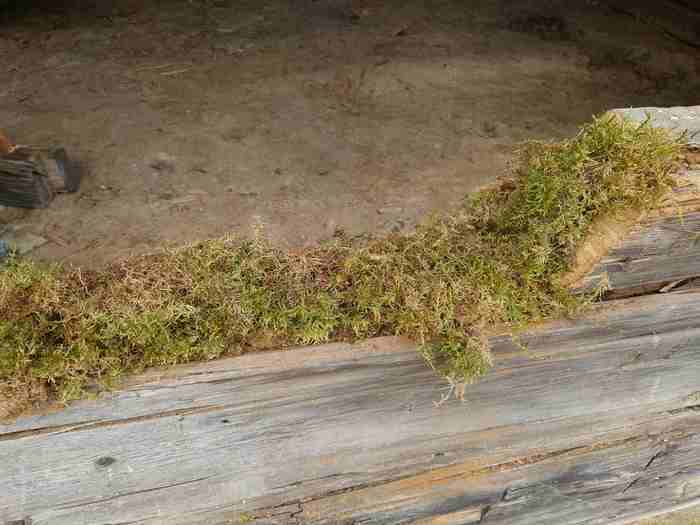
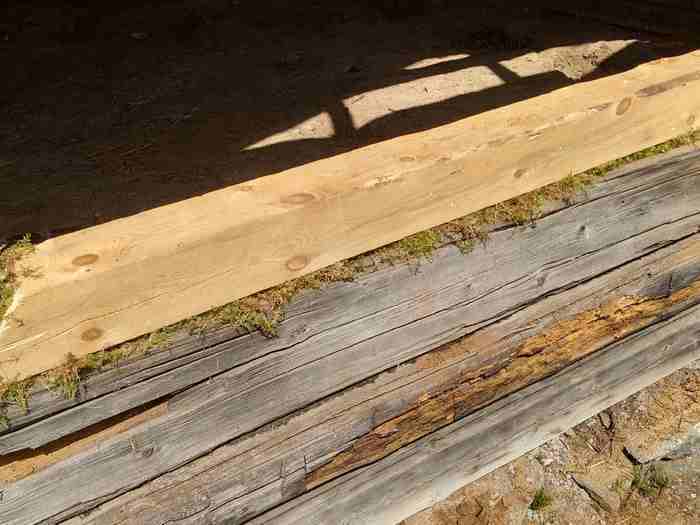



When renovating log homes, diffusion-proof insulation such as rock wool, mineral wool or Glava must not be used. These retain moisture and will mold. It is important that moisture can diffuse through the log wall without condensing in the insulation. We found that Hunton wood fiber insulation is an excellent product that does just this:
- It is approved as modern insulation,
- has enormous insulation value,
- satisfies fire requirements (wood fiber chars and therefore does not burn),
- is short-lived and uses the edge of wood that would otherwise not be used,
- can be reused or recycled without creating special waste,
- is available in loose weight for blowing in or as blocks that can be cut with a large knife by hand,
- heat storage capacity in contrast to "light" insulation.
- Insulation against sun and heat in the summer that creates a stable indoor climate,
- has good sound insulation properties,
- can be handled without gloves/face masks and
- costs the same as, for example, Glava/Rockwool.
In short, the perfect product for anyone who wants to build healthy and sustainable.
The U-value calculator shows that a 20cm additional insulation on the old lath wall provides an insulation capacity better than today's Tek17 building requirements (≤ 0.22 W/(m2 K):

It looks like this:
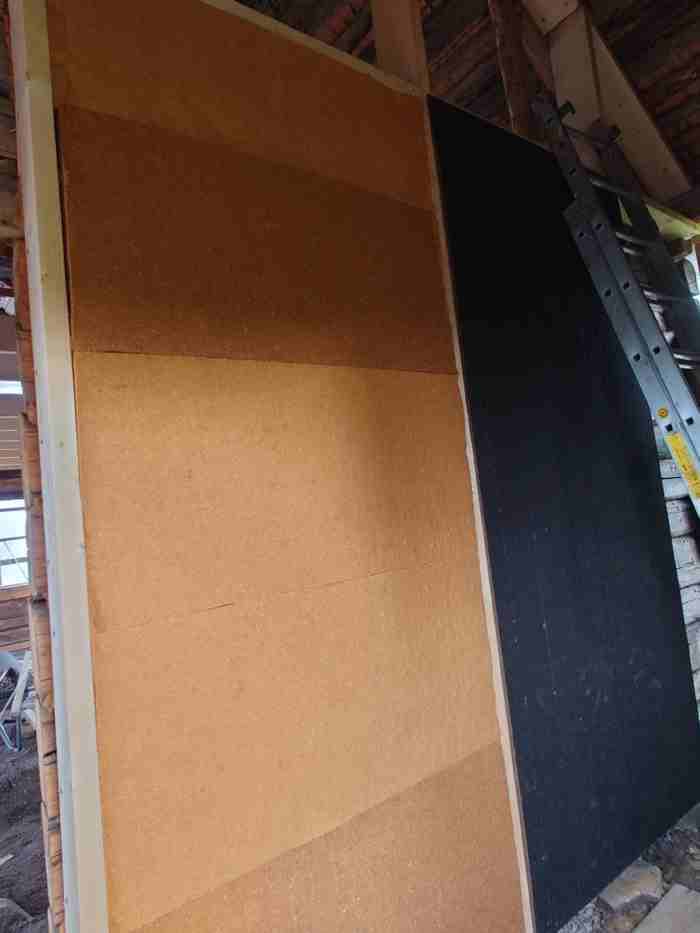

As a natural product, it has color nuances, on the right side already covered with asphalt / cardboard slabs. These are taped at the joints with diffusion-permeable tape.
Here, an example of a wall under rehabilitation:
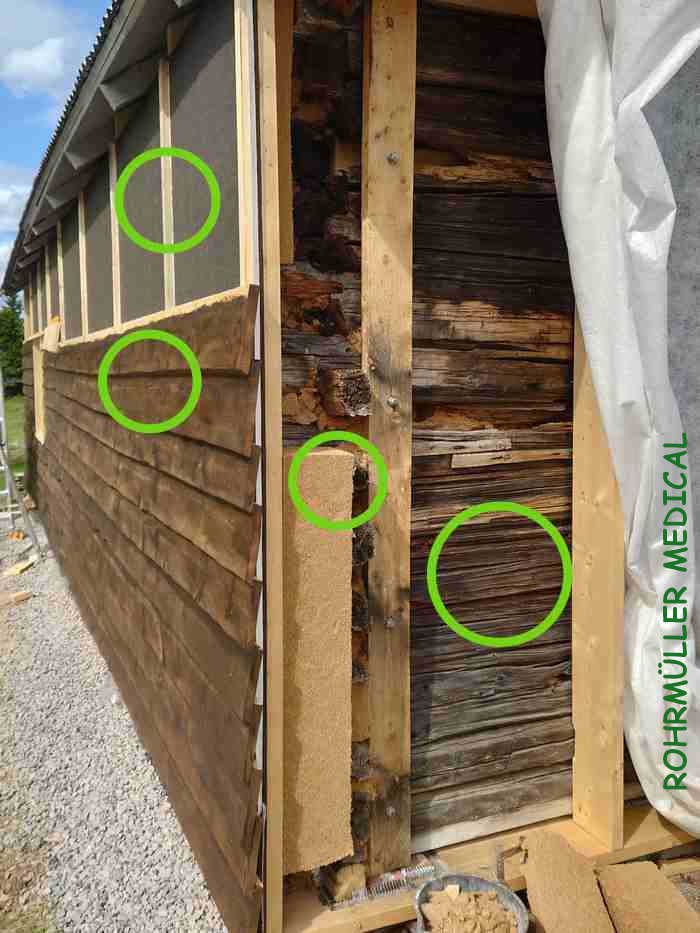

- The timber is exposed to the inside of the room, allowing moisture to dry out and the original timber wall is preserved.
- The outside of the timber is insulated throughout with Hunton wood fibre insulation.
- Asphalt sheets are nailed on and taped for windproofing
- Racking so that air can circulate
- Norwegian timber paneling creates a robust barrier against the elements, is durable, beautiful to look at and is based on traditional craftsmanship.
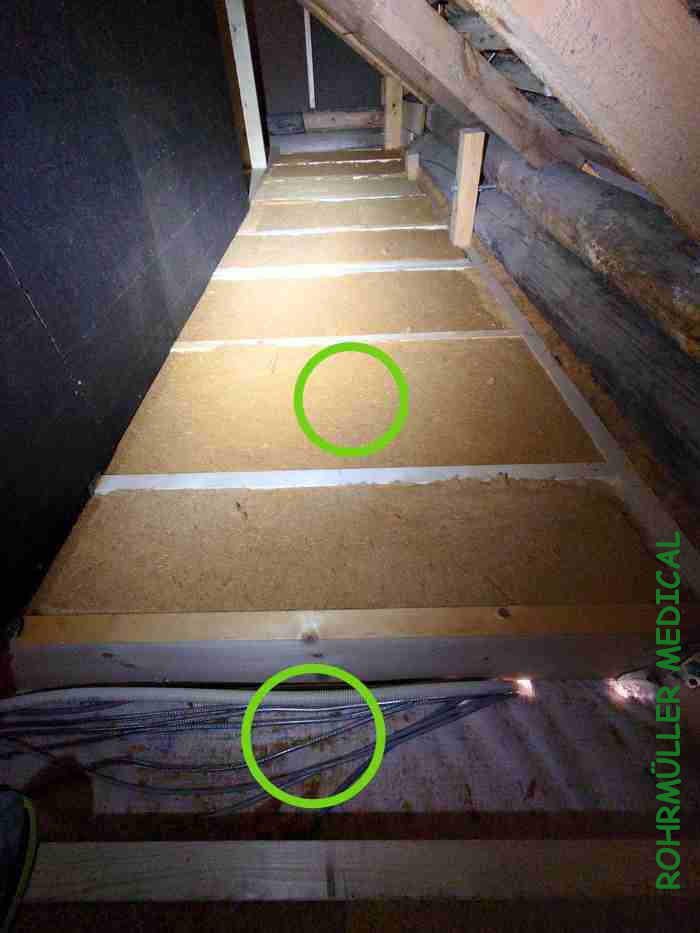

The roof is built up in a similar way. The difference is the diffusion-open vapor barrier under the roof panel, with HUNTON wood fiber insulation on it. Blown-in insulation could also have been used here. To avoid thermal bridges where the beams run, an additional layer of insulation is placed over it, tightly sealed.
Note the shielded cabling in its own shaft that enables changes / access to the installation later if necessary. Empty pipes for pulling network cables, fiber, etc. are presented in the next section.
Electrical installation
When rehabilitating, retrofitting or new installation, it is recommended to use shielded cabling that is grounded on one side. Here you see a complete shielded house installation (supply to the rooms). This enables insulation / disconnection of areas in the house.
Shield insulation in the cabling has the additional effect of significantly limiting the risk of fire, for example, if the power cable were accidentally nailed through - the nail will then always have contact with ground and trigger the earth fault circuit interrupter.
On the right side is unshielded cabling to the heat pump and garage. These are located far away from the sleeping areas and living areas, so to save money, "regular" (unshielded) cabling was used.
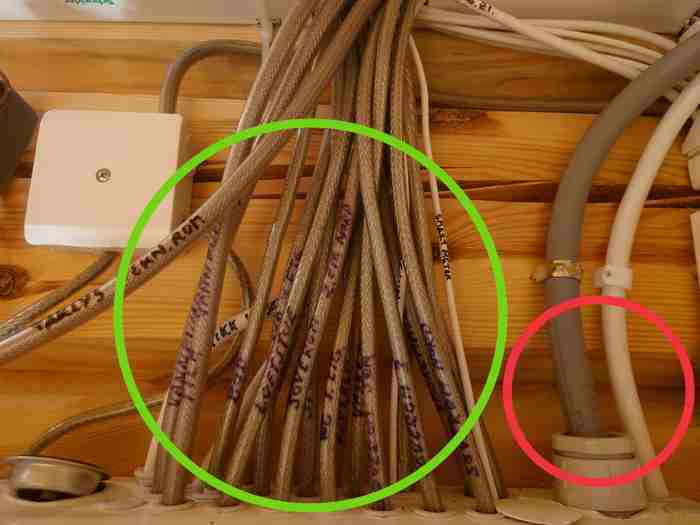
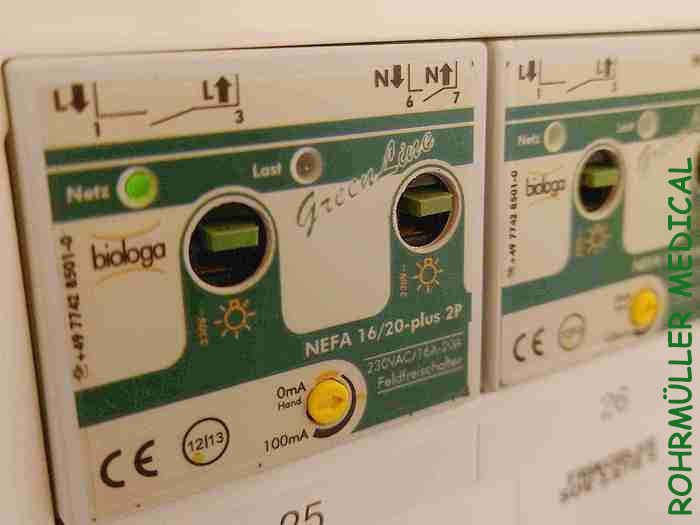
If you want to make sure that the power is COMPLETELY off, and that you do not get an electromagnetic load from sockets at the head end, you can install mains disconnectors in the fuse box: They sense when the last consumer in the room is turned off (e.g. the bedside lamp in the evening) and then cut the power. Using a weak voltage that runs across the conductors, it senses as soon as a light switch is operated and reconnects the power.

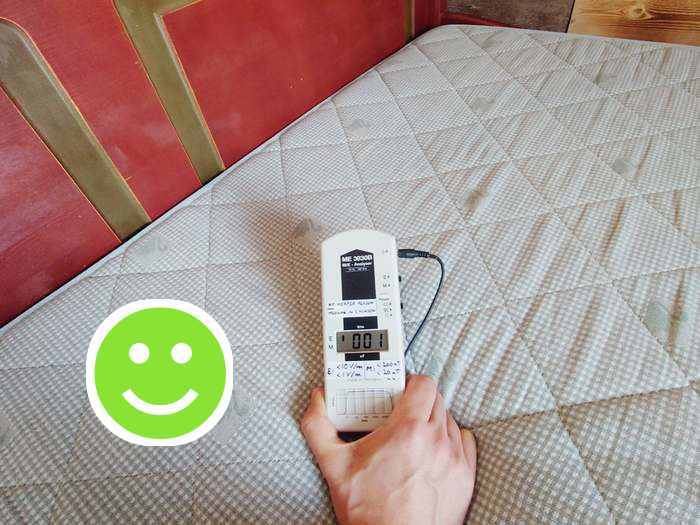
This leads to low alternating electric fields (1 V/m):

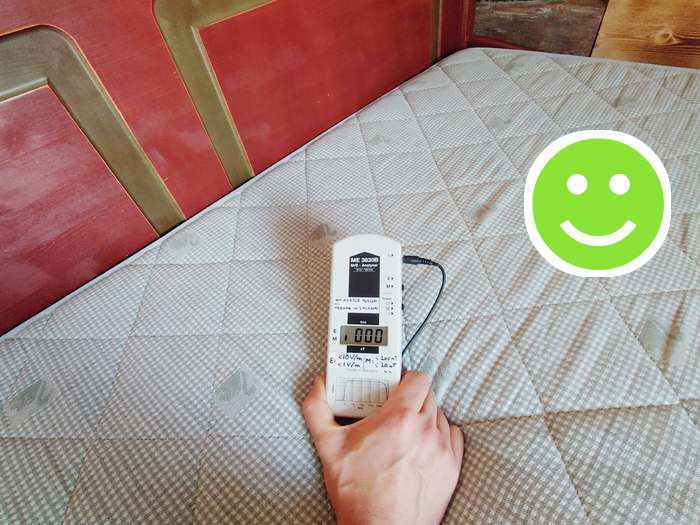
and alternating magnetic fields (0 nT):

AMS meter (smartmeters) and measurement results
Smartmeters installed in Norway create their own mesh network on a high-frequency band that is constantly sending, meaning all meters continuously send pulsed signals in the GHz band. This way you get continuous electricity consumption (and billing) around the clock that is so specific that you even can see which appliances are currently in use, based on their signature/consumption. You can also remotely disconnect the meter. It would be speculative whether the choice of this type of meter was economically motivated, since there are AMS meters that transmit via the power grid, only once a day, or can be connected to the Internet via Ethernet. Such technology is standard in other European countries.
Most people who do not want AMS meters for reasons of health, the precautionary principle against a technology with a high potential for harm or on the basis of privacy must go through a GP or psychologist who must certify that "the patient feels discomfort" or similar wording that insinuates a psychological problem. This could then result in the electricity company disconnecting the transmitter module in the meter.
If you do not want to go this route, e.g. because you do not want to be called ill (actually mentally challenged) or because you need the AMS meter with a communication module to be able to produce electricity that is fed into the power grid (whether solar panels are a good investment so high up is another question), you must go another way: Move the meter away from the fuse box in the house / house wall and equip it with a directional outdoor antenna. This does not solve the problem of the EMF pollution on neighbors and biology (ref. pollinating insects), but in rural areas this is an alternative. It requires space on the property and a "suitable" positioning of the power feed line.

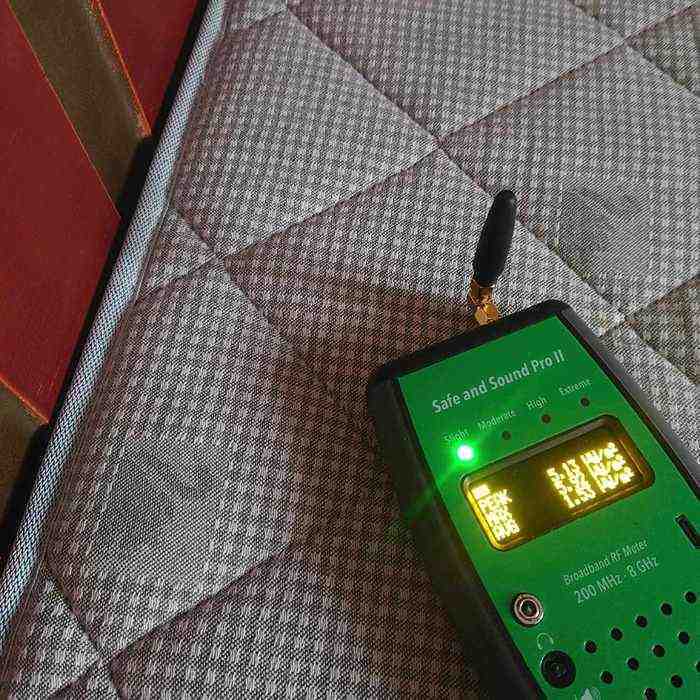
This is the high-frequency radiation level indoors in the sleeping areas. The room below has a double-glazed window with a clear view of the transmission tower (5G network, full coverage). If necessary for people who are hypersensitive to electricity, the window could be shielded, for example with a shielding curtain (woven silver wire).

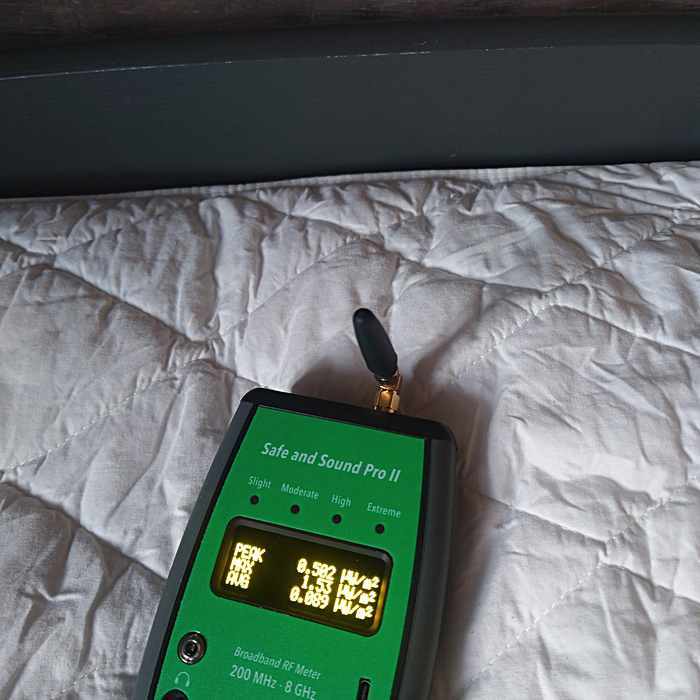
Another room that has a very low value, 0.5 μW/m². The extra shielding comes from lightweight walls insulated with Hunton wood fiber insulation:

This room also has coverage and Internet access (wired network) and would be well suited as a bedroom for children or very sensitive people.
Installation of lamps and light switches
A ceiling lamp shows an unacceptably high alternating electric field (179 V/m) during operation:
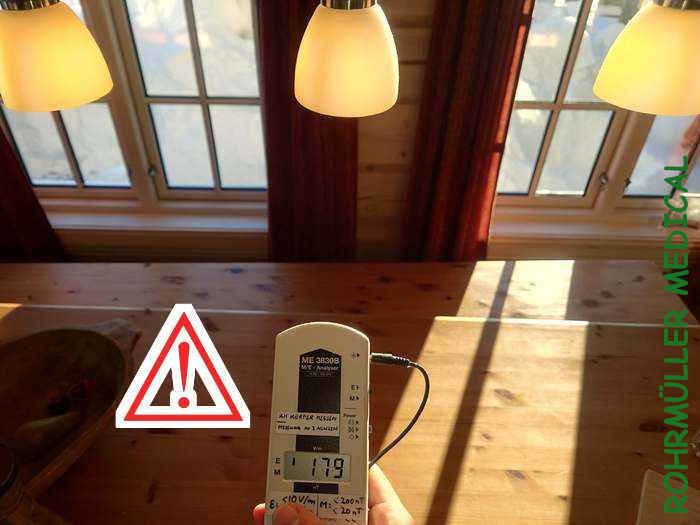

Even when turned off, the values are still too high (45 V/m):
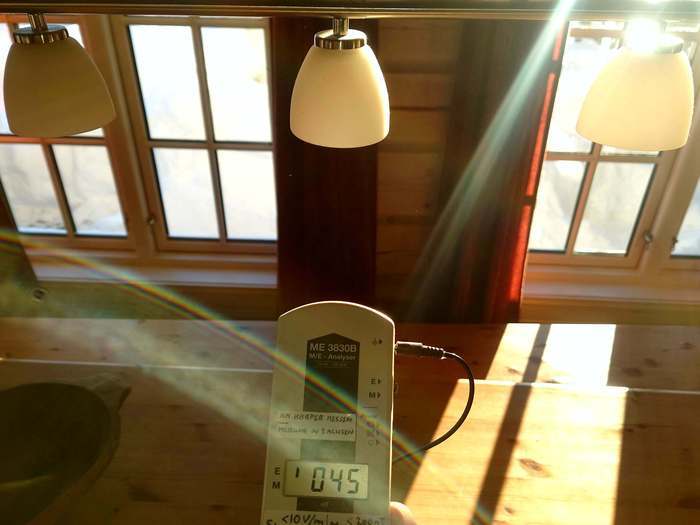

It turns out that the light switch in the room is single-pole (a so-called toggle switch) in order to be able to turn the light on/off from different places. This means that there is always electricity in the wire, even when the lights are off. In Norway you can identify such switches by the fact that they have no markings (no numbers) on the switch panel:

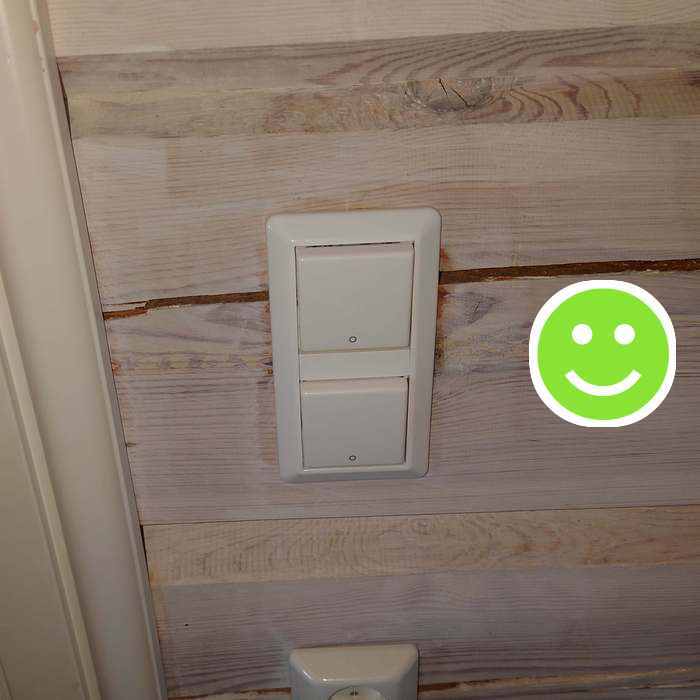
This switch was replaced with a 2-pole switch. In Norway they have a "0" number in the lower (off) position. Both current conductors are thus broken and no current can flow:

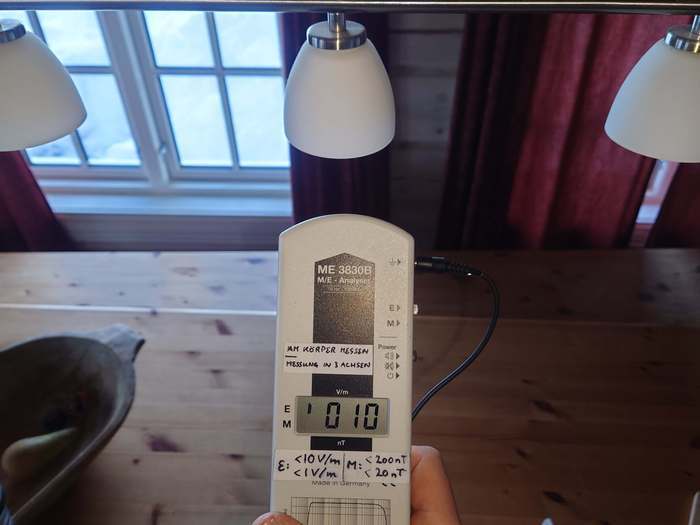
Furthermore, it turned out that the lamp fixture, although made of metal, did not have a a grounding wire connected to it (the green/yellow conductor), although there is no technical reason for this. This was easily solved by crimping a cable lug onto the ground conductor and attaching it to the metal base from which the lamp hangs:

Result: The alternating electric field in the "off state" became 10 V/m in the immediate vicinity, i.e. less than 1/4 of the original value:

and 18 V/m when it is on. That was 1/10 of the initial value (from 179 to 18 V/m)! Remember that the meter should be held where the head/body is, so the actual electric field load on people sitting around the table is even lower.
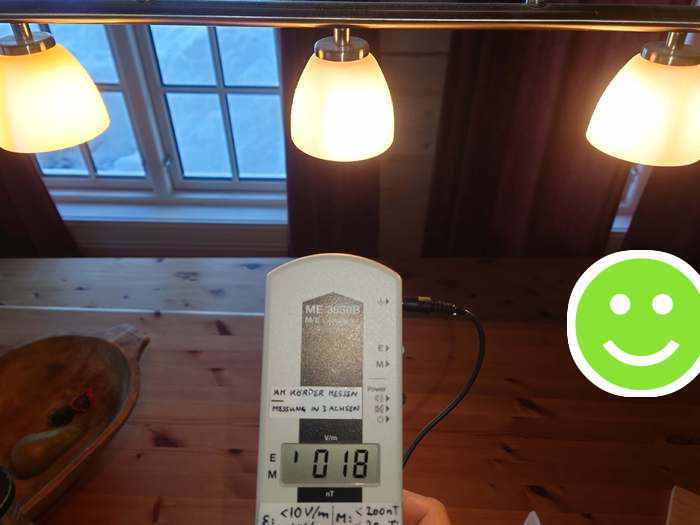

Many lamps and fixtures can easily be converted this way. At the same time, contact safety is increased. This should be a given when goods are imported by electrical companies to Norway (CE / VDE) and installed by an approved electrical installer, which is unfortunately not always the practice.
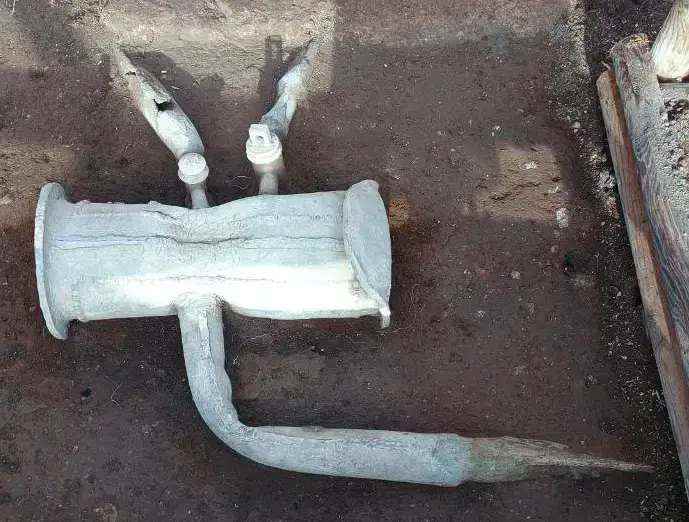
Pipe installation
The following image shows pipe elements that can contain up to 2.5% lead and 0.5% arsenic, so-called dezincification-free (DZR) brass:
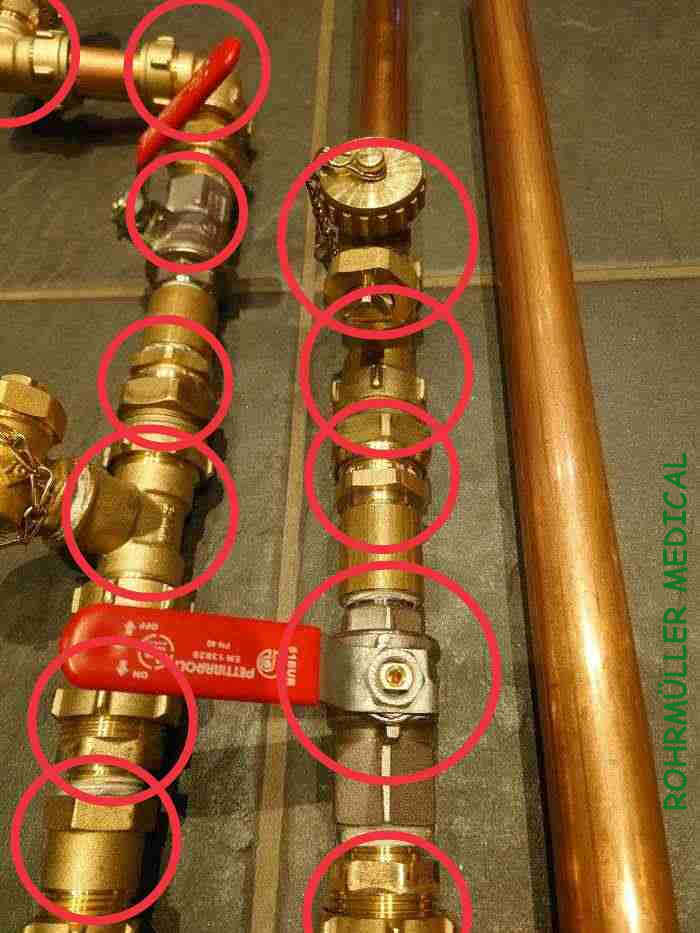

These are common in today's home installations. One way to protect yourself from a possible load of heavy metals and other toxins is to use an RO filter or to distill drinking water AT THE FAUCET.
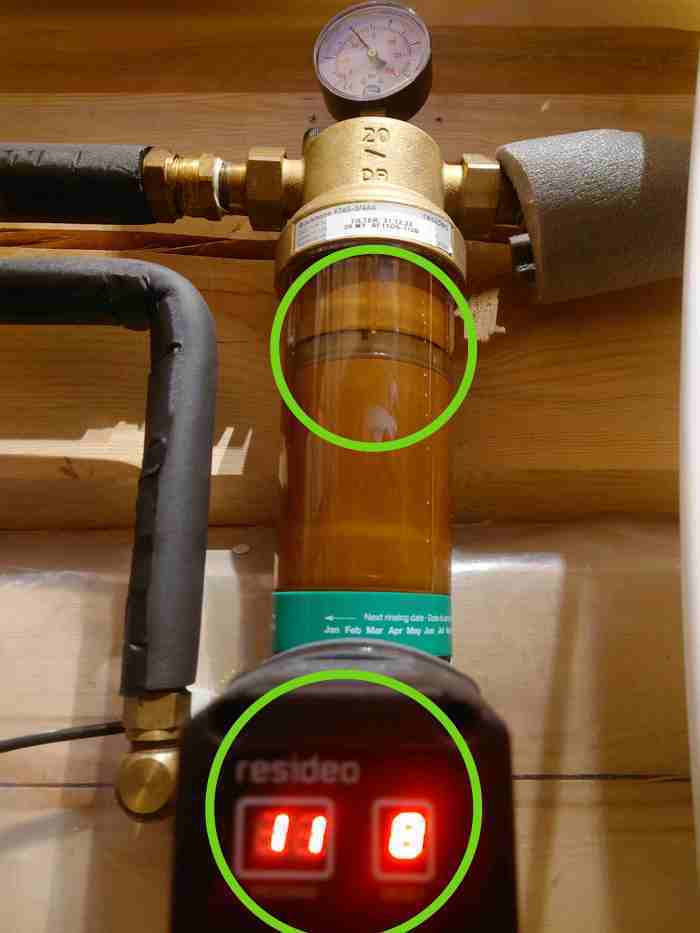
The water intake is often equipped with a pre-filter, especially for buildings that have their own well. These pre-filters are often made of plastic that must be replaced frequently. This causes bacterial growth in the filter element and produces a lot of waste that is difficult to recycle (plastic element saturated with sand and silt).
A stainless steel pre-filter with automatic flushing is an alternative:

Heating installation
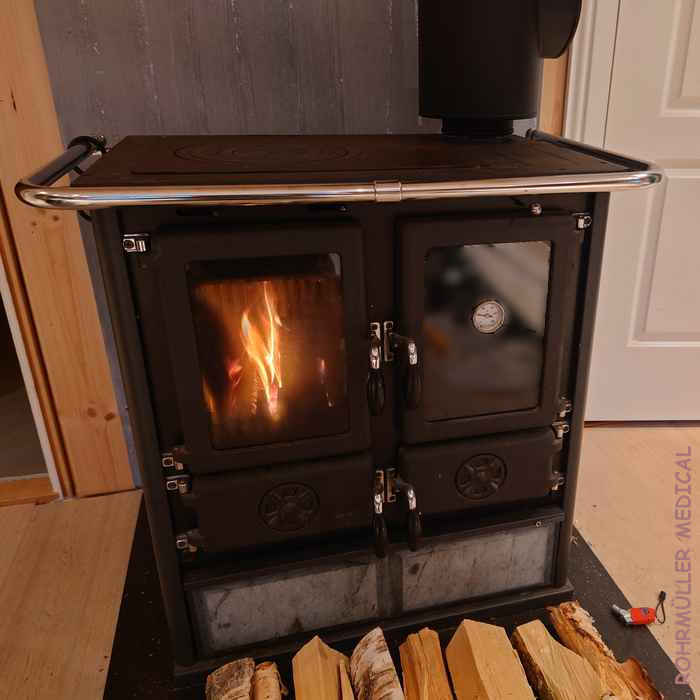
Installing a clean-burning wood stove provides:
- Heat regardless of electricity and electricity price. The ability to store wood allows you to control costs better than electricity.
- Ability to cook without the use of an induction stove (magnetic field) or gas.
- High efficiency compared to older stoves due to complete combustion.
- educed wood requirement compared to older stoves.
- One-time cost with low maintenance costs.
- An independent heat source, as long as you can get wood.
- Some heat storage depending on the model if it has soapstone elements.
Similar models like the example below are regularly available on the used market (Finn.no) at 1/2 the price of new if you have a little patience. These also maintain their resale value.

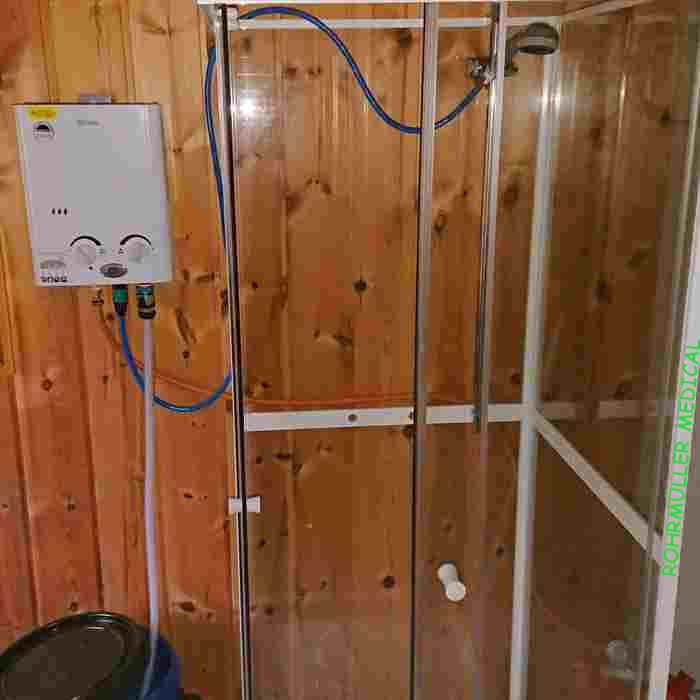
If you are considering living completely without electricity, want to limit electricity consumption, want to use hot water in a cabin that does not have running water or is not regulated for the discharge of grey water (such as from showers and sinks), you can go the following way:
Install a gas water heater. It heats water instantly up to 79°C without any problems and is economical to use. You can use a water barrel (bottom left in the picture) with a simple DC pump. The gas tank can be seen at the bottom right in the picture. It is recommended to install a CO (carbon monoxide) meter for safety reasons.

If you have any questions or suggestions about building in a healthy way, please use the comments field, or take contact.
Are you looking for / need a timeout / place without high radiation exposure, with few environmental toxins and close to nature, please take contact!
SOME SOURCES AND FURTHER INFORMATION, no guarantee is given for content or accuracy:
German Building Biology Focus Areas
https://www.verband-baubiologie.de/images/baubiologie/25_Leitlinien_der_Baubiologie.pdf
Building Biology Guidelines for Sleeping Areas (2024), in German
https://www.verband-baubiologie.de/images/downloads/SBM-2024-RICHTWERTE.pdf
Pipe Installations
https://www.kemifokus.dk/bly-og-nikkelafgivelse-til-drikkevand-fra-ventiler-og-vandhaner-af-messing/
Sintef
https://blogg.sintef.no/industri/blyfri-messing-rent-drikkevand/
Directorate for Radiation Protection and Nuclear Safety (State Limit Values)
https://dsa.no/
EUROPAEM EMF Guideline 2016 for the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of EMF-related health problems and illnesses
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27454111/
EMF Source collection, research (in Norwegian, but with European / international sources). 2024.
EMF Consult.
https://emf-consult.com/
FELO - Association for Electro-sensitive people
https://www.felo.no/
EU: Panel for the Future of Science and Technology (STOA)
https://www.europarl.europa.eu/stoa/en/home/highlights
Arbeidstilsynet. Limit values, Ministry of Labour and Social Affairs, 2024.
https://www.arbeidstilsynet.no/regelverk/forskrifter/forskrift-om-tiltaks--og-grenseverdier/
Arbeidstilsynet. Limit value for 1,2-dichloroethane, May 2021, Revision of Directive 2019/130/EU
https://prod.arbeidstilsynet.no/globalassets/tema/kjemikalier/grunnlagsdokumenter-for-grenseverdier-for-kjemikalier/d/12-dikloretan-grunnlagsdokument-2021.pdf
Norwegian Association Against Noise
http://stoyforeningen.no
Infrasound noise measurement
http://www.redvoxsound.com/
Back


All comments are moderated before being published. Your email will not be visible